Ariella Pharmaceuticals
A

Nominsen®
Nominsen® is an allele selective antisense oligonucleotide (ASO) drug, and its non-proprietary name is ASO67. The antisense oligonucleotide (ASO) is referred to the single nucleic acid strand which makes up of chemically modified DNA molecules, further binds to the complementary RNA (9). It primarily targets the single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) rs362307 in exon 67 of mutant HTT gene. The rs362307 is present in ~40% of the Huntington’s Disease (HD) cases from European ancestry with a variant GC pair (10, 11).
Targeting mutant HTT gene
Our focus is on the direct targeting of the mutant HTT (mtHTT) gene, considered the causative mutation of HD. The expanded CAG repeat in the mtHTT is transcribed as part of full-length mRNA and HTT exon 1 fragment mRNA, giving rise to toxic full-length mutant Huntingtin (mHTT) and toxic exon 1 protein. To address this, we utilise the mechanism of ribonuclease H (RNase H) degradation. RNase H is an enzyme found in eukaryotes responsible for RNA cleavage in the presence of an RNA-DNA heteroduplex, a double-strand mixture with DNA and its complementary RNA molecules (12). The RNA-binding domain of RNase H recognises the RNA-DNA heteroduplex, cleaving the complementary RNA strand (12). The remaining uncleaved DNA strand is then released, resulting in the degradation of the RNA strand (9). In this case, a synthetic single-stranded DNA molecule, complementary to the pre-mRNA of mtHTT, is designed to silence the expression of mtHTT.

Figure 2. The mechanism of mutant HTT gene and the RNase H degradation.
Click the video to see how does RNase H bind to the RNA-DNA heteroduplex (13)
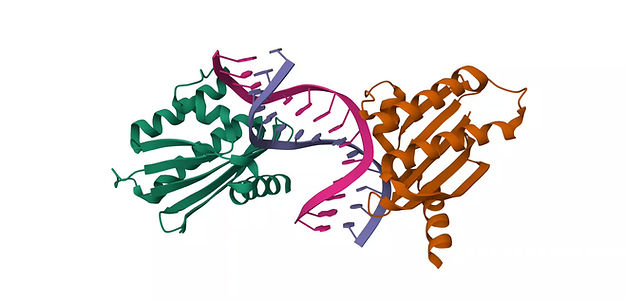
The biological function of the wild-type huntingtin (wtHTT) protein is yet to be known. However, multiple studies indicated that loss of wtHTT could lead to abnormal cellular function, and the affected individuals with less wtHTT are seen to have more severe symptoms (4). Thus, to achieve allele-selective targeting of mtHTT, we aimed to select sequences that differ between the mtHTT and wtHTT. Multiple genetic-wide association studies have highlighted the presence of a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) rs362307 within the pre-mRNA of the mtHTT, where SNP is the most common human genetic variant with a single base pair (8, 10, 11). This rs362307 is found to have a high prevalence in approximately 40% of affected individuals compared to unaffected populations (8, 10, 11). By targeting rs362307, we can selectively eliminate the mHTT with negligible effects on the wtHTT. Our approach represents a precision strategy, offering new possibilities in the treatment of Huntington’s disease.

Figure 3. The location of the SNP re362307 in mutant HTT gene in the Chromosome 4.

ASO67's administration and action
ASO67 is administrated via lumbar intrathecal injection, which directly reach the brain from spinal cords without bypassing the blood-brain barrier, and transport via cerebrospinal fluid to be widely distributed around the central nervous system (CNS). Lumbar intrathecal injection is a clinical familiar and widely acceptable methods for administration (4).
A simple video illustrating the animation of lumbar intrathecal injection (17):
Upon injection, ASO67 efficiently enters cells by fusing with plasma membranes and translocating into the nucleus. It specifically binds to rs362307 in the pre-mRNA of the mutated HTT (mtHTT) gene, forming a DNA-RNA heteroduplex. This heteroduplex is then recognized by RNase H, leading to the cleavage of the pre-mRNA of the mtHTT. The cleaved pre-mRNA becomes unstable and is subsequently degraded. The unbound wild-type HTT (wtHTT) gene continues to be transcribed and translated, resulting in the synthesis of wild-type huntingtin protein (wtHTT). Ultimately, this process silences the mtHTT, allowing the continuous expression and translation of the wtHTT gene to produce the wtHTT.
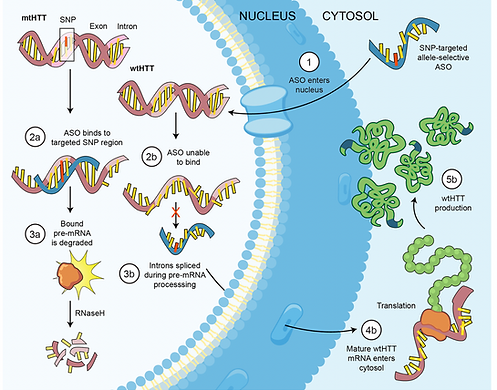
Figure 4. The action of ASO67 after injection and entering the cells (12).

Results from clinical trials : Promising effects
The recent allele-selective Antisense oligonucleotide drug (WVE-120101) aimed to target the rs362307 had failed to meet the clinical efficacy and halted due to poor Phase I clinical results with inconsistent mtHTT lowering and lack of dose-dependent response (4).
Phase III clinical trial: Our developed drug, Nominsen® has achieved a long-term clinical efficacy and tolerability with consistent lowering levels of mutant Huntingtin within the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) with 35% in treated patients compared to placebo group, with an improved motor, cognitive behavior with respect to results from the digital biomarkers, which are digital measurements for evaluating the motor signs and cognitive functions (4). Additionally, we also observed increased cortical volumes from structural MRI.

Disclaimer: the clinical result for Nominsen® is fictional and it was created for University College London's BIOC0015 coursework.


